Energy transition represents a $14 trillion uncertainty for upstream oil and gas
Oil and gas is a risky business. Over the years, those risks have been tempered by a single tenet – that demand would continue to rise indefinitely. As the energy transition gathers momentum, that belief has all but evaporated. Oil demand may continue to grow for another decade or more. On the other hand, if the world acts decisively to limit global warming to 2°C by 2050 – Wood Mackenzie’s accelerated energy transition (AET)-2 scenario – oil demand and prices would fall rapidly later this decade. Gas demand and price, however, would be more resilient.
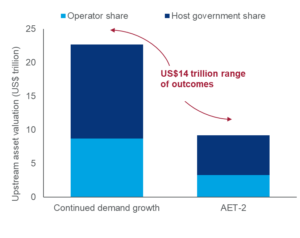
While this range of outcomes has major implications for the oil and gas industry, in either scenario there is still a huge amount of upstream value on the table. In a new report, Wood Mackenzie asserts that the range of pre-tax future valuations for upstream is a staggering $14 trillion – from $9 trillion to $23 trillion. On a post-tax basis, operators’ share of this economic rent ranges from $3 trillion to $9 trillion.
“The industry now finds itself having to supply oil and gas to a world in which future demand – and price – are highly uncertain,” said Wood Mackenzie VP Fraser McKay. “The range of possible outcomes is dizzying. But the world will still need oil and gas supply for decades to come, and the scale of the industry will remain enormous.”
In this macro environment, Wood Mackenzie believes delivery and discipline will be paramount in all aspects of the upstream value chain. While performance against budgets and timelines has improved dramatically since the last downturn, the industry will need to remain relentless in its push to improve efficiency, drive down costs and deliver projects flawlessly. Oil and gas companies need to send a strong signal to stakeholders that they can be reliable stewards of capital.
“Only exceptional, low-cost projects will work in all demand scenarios. Inevitably, the cost of capital and the cost of doing business in oil and gas will increase,” said Wood Mackenzie Research Director Angus Rodger.
Oil and gas companies also must improve their ESG credentials. For the biggest players, new energies will play an increasing role, but this is a not an option for many industry participants. They will need to cut Scope 1 and 2 emissions to reduce their exposure to increasingly expensive debt.
Investment will shift to gas, ending oil’s long supremacy. “The industry will have to figure out the conundrum of weaker economics if the giant gas projects the world needs are to happen,” Mr Rodger said. “The returns on developing a barrel of oil are currently higher, with oil-production and cash-flow profiles delivering more value upfront. Gas prices are lower than oil prices on an energy-equivalent basis; that relationship will have to invert as it does in our AET-2 scenario to make this happen.”




